Welcome to Mouyis Medical Center
Keeping Hearts Beating Strong
We offer investigation and treatment for general medical and cardiological conditions

Location
24-26 A/B Larnakos Avenue, Nicosia 1035
Phone
+357 22 438122
Info@mouyismedical.com
the experts
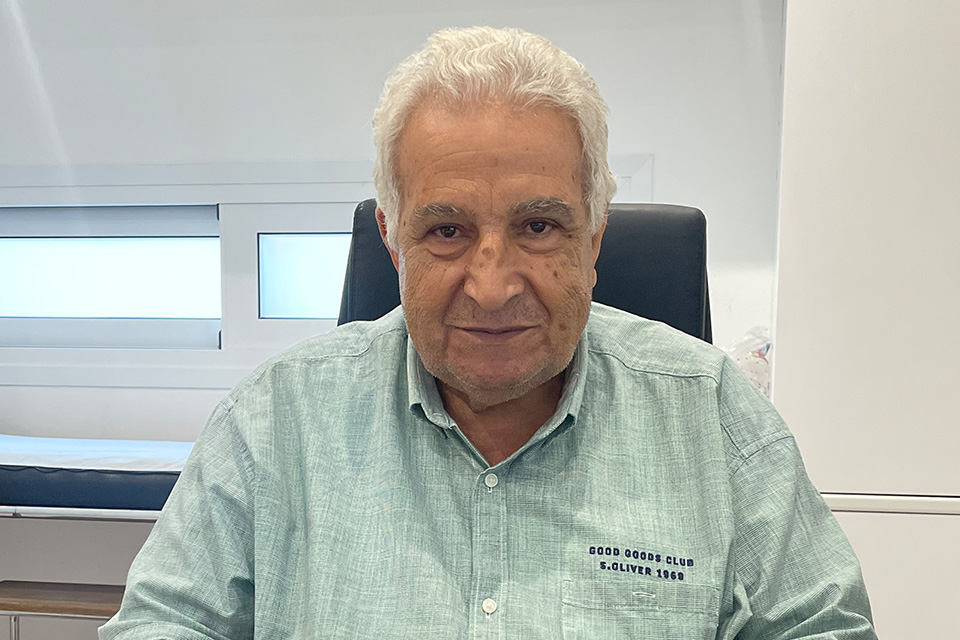
Meet Your Doctor
Our doctors are here to provide you with the highest standard of medical care, ensuring you receive the attention and treatment you deserve.
Cardiology Consultant
BM BCh (Oxford), MA (Cambridge), MRCP(London), CCDS (IBHRE)
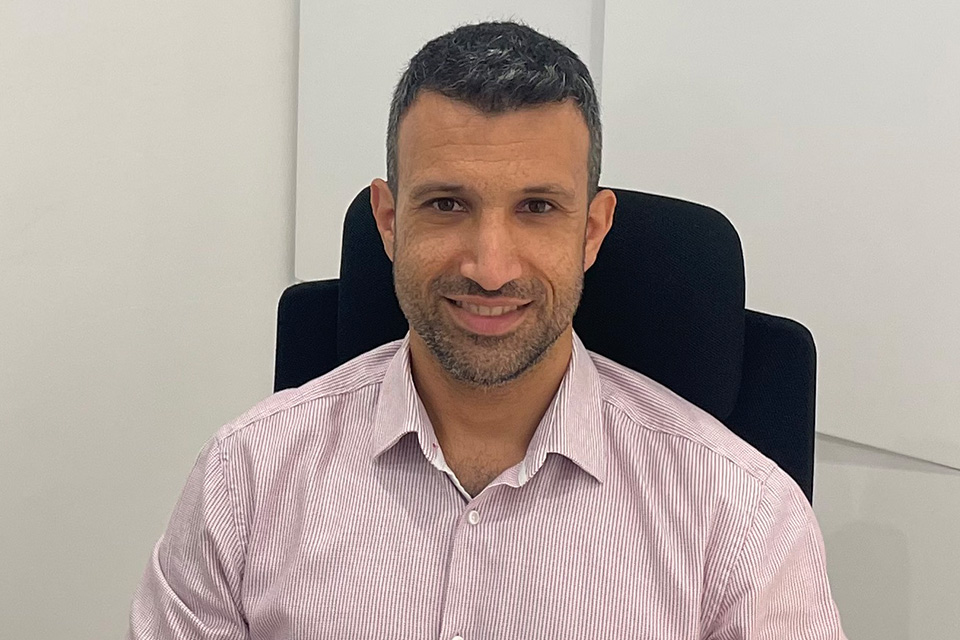
the experts
Meet Your Doctor
Our doctors are here to provide you with the highest standard of medical care, ensuring you receive the attention and treatment you deserve.
Cardiology Consultant
BM BCh (Oxford), MA (Cambridge), MRCP(London), CCDS (IBHRE)
About us
Your Health,
Our Commitment
Our medical centre was established in May 2024 in a newly renovated space. We combine general medical and cardiological services and expertise in one building. We are located very near the centre of Nicosia at Larnacos avenue. We operate within the General Health System (GESY) but patients not eligible also welcome.
Diagnostics
Years Experiences
Conditions
Advanced Medical & Cardiology Diagnostics
We offer investigation and treatment for general medical conditions and a number of cardiological conditions.

Chest Pain/Angina
Chest pain due to coronary artery disease is when a narrowing in the arteries supplying the heart causing inadequate supply during conditions of physical exertion (e.g. when exercising). It is characterized by a squeezing sensation in the chest that is relieved with rest or appropriate medications and can also spread to the left arm or the jaw.
Angina can be diagnosed by a stress test such as a treadmill exercise test (or other appropriate tests) and is treated by medications or invasive procedures to implant stents in the coronary arteries during cardiac catheterization.
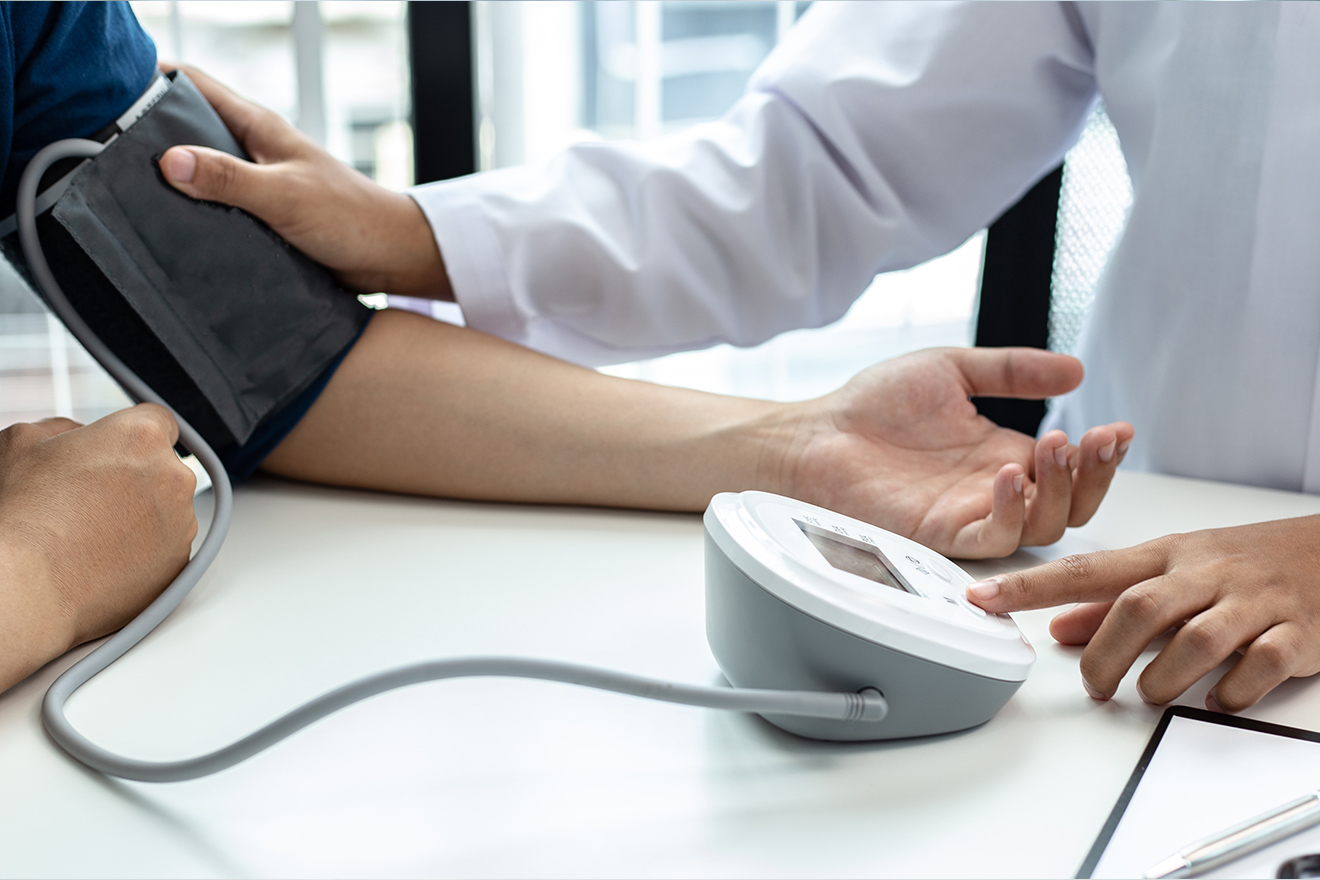

High Blood Pressure
Hypertension (or high blood pressure) is when the blood pressure inside the arteries in the body is consistently elevated. It is most commonly idiopathic with no clear cause identified (primary hypertension) but it can also be caused by other conditions (secondary hypertension). It requires blood pressure measurement over 24hrs or over many days at home to diagnose.
Hypertension is causative to a multitude of cardiovascular conditions such as coronary artery disease and heart attacks, stroke, renal failure, arrhythmias. It is treated with lifestyle measures such as weight loss and reduction in salt intake and medications which can be titrated to achieve appropriate measurements
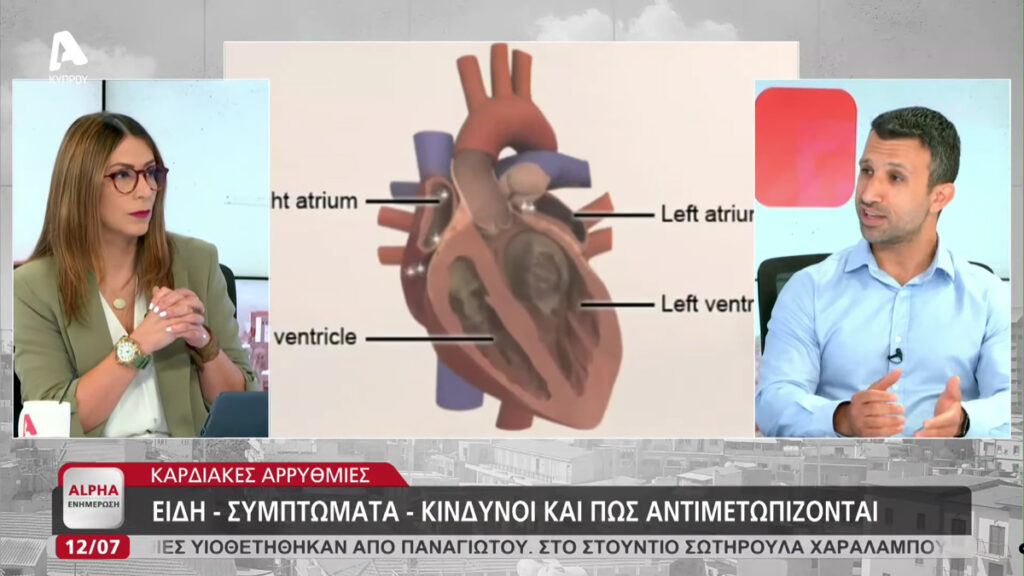
Valvular Heart Disease
The heart contains four valves that ensure unidirectional flow of blood along the heart chambers and the blood vessels. These valves can have problems or become damaged and become either tight (Stenotic) or incompetent (regurgitant).
Most commonly this is due to age, heart attacks, infection or other diseases but can also be present congenitally. The most common valvular diseases are mitral valve regurgitation and aortic valve stenosis.
Clinical examination, echocardiogram and ECG can diagnose heart valve disease and appropriate management can then be initiated.

Heart Failure
Heart failure is the inability of the heart to pump enough oxygenated blood to the body to ensure appropriate oxygenation of the tissues. It is usually caused by a weakness of the heart muscle or by impaired relaxation of the heart muscle. Symptoms include fatigue, shortness of breath, exercise intolerance and swelling of the legs.
The most common causes are heart attacks, valvular heart disease and genetic causes such as thickening or dilatation of the heart. It is diagnosed with clinical examination, ECG and echocardiography. The treatment is medications and interventions to address the underlying aetiology. Cardiac devices such as ICD or CRT can be used to treat and protect patients with heart failure.
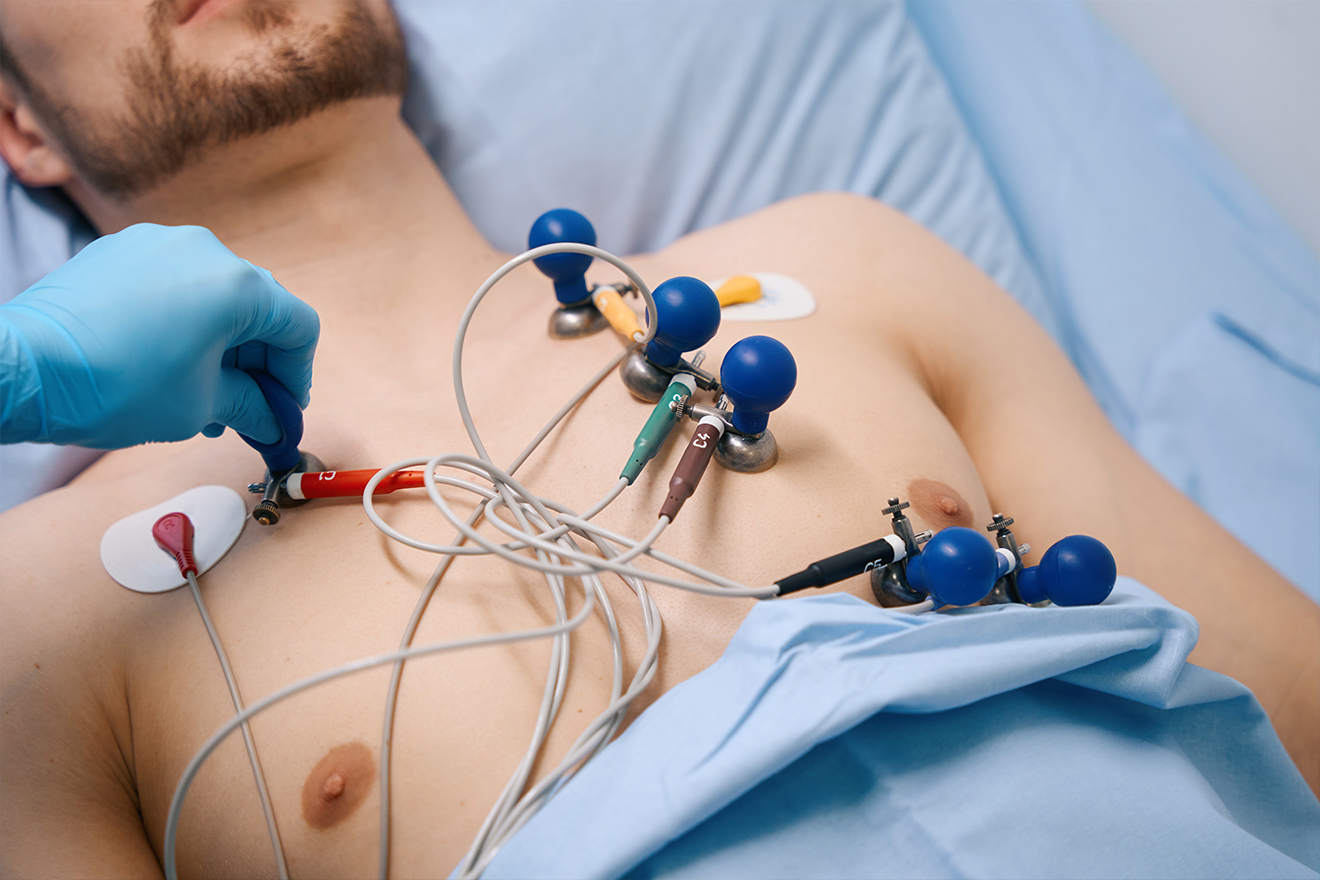
Atrial Fibrillation
Atrial fibrillation is an arrhythmia where the top chambers of the heart (Atria) contract rapidly and irregularly and causes irregular contraction of the bottom chambers (ventricles) as a result. It is the most common arrhythmia in the population and increases in prevalence with age.
It often causes symptoms of palpitations or chest pain. Diagnosis can be made with an ECG or with a 24 or 48hr recording of the heart rhythm (Holter monitor).
Treatment is focused on preventing complications such as stroke and alleviating symptoms.

Sports and Exercise
Exercise is crucial in ensuring long term health and is beneficial for people of all ages and abilities. Both cardiovascular exercise and weight training should be performed and both moderate and intense periods of exercise are recommended.
Studies have shown that exercise capacity is an independent predictor of a long and healthy life. People who participate in competitive amateur or professional exercise/sports should have cardiac screening to ensure there are no underlying cardiac conditions.
Exercise can also be undertaken in the presence of cardiac conditions however the frequency and intensity may need to be adjusted depending on the exact diagnosis.

Cardiac prevention
Most cardiac conditions happen over a prolonged period of time and can be prevented by investigating and treating the causes at an early stage. Examples of important risk factors include elevated cholesterol, high blood pressure, presence of diabetes mellitus and smoking. Lifestyle measures such as exercise and appropriate diet are also important.
Appropriate tests such as blood tests, ECG and clinical examination can help identify and optimize these conditions.

Cardiac prevention
Most cardiac conditions happen over a prolonged period of time and can be prevented by investigating and treating the causes at an early stage. Examples of important risk factors include elevated cholesterol, high blood pressure, presence of diabetes mellitus and smoking. Lifestyle measures such as exercise and appropriate diet are also important.
Appropriate tests such as blood tests, ECG and clinical examination can help identify and optimize these conditions.
Prevention by Investigating and Treating at an Early Stage
Cardiac tests
Diagnosing for a Healthier Heart
We offer specialised non invasive cardiac investigations to help diagnose and treat a variety of cardiac conditions. All the tests are supervised by Dr Kyriacos Mouyis.
A Holter monitor is a small device that can record the heart rate and rhythm for a period from 24 hrs. up to 7 days. It is essentially a longer ECG that allows the doctor to make a diagnosis of heart rhythm problems where that is suspected.
The Holter monitor is attached with stickers onto 7 points on the body. It is important that the patient does not take a shower or a bath as this may cause the stickers to come off or the machine to malfunction.
Holter monitoring is often done for symptoms of palpitations or when the doctor suspects an arrhythmia may a be significant part of your disease process.
After fitting the monitor, you will need to return the next day to have it removed. Then the doctor needs to review and analyze the results before discussing them with you.
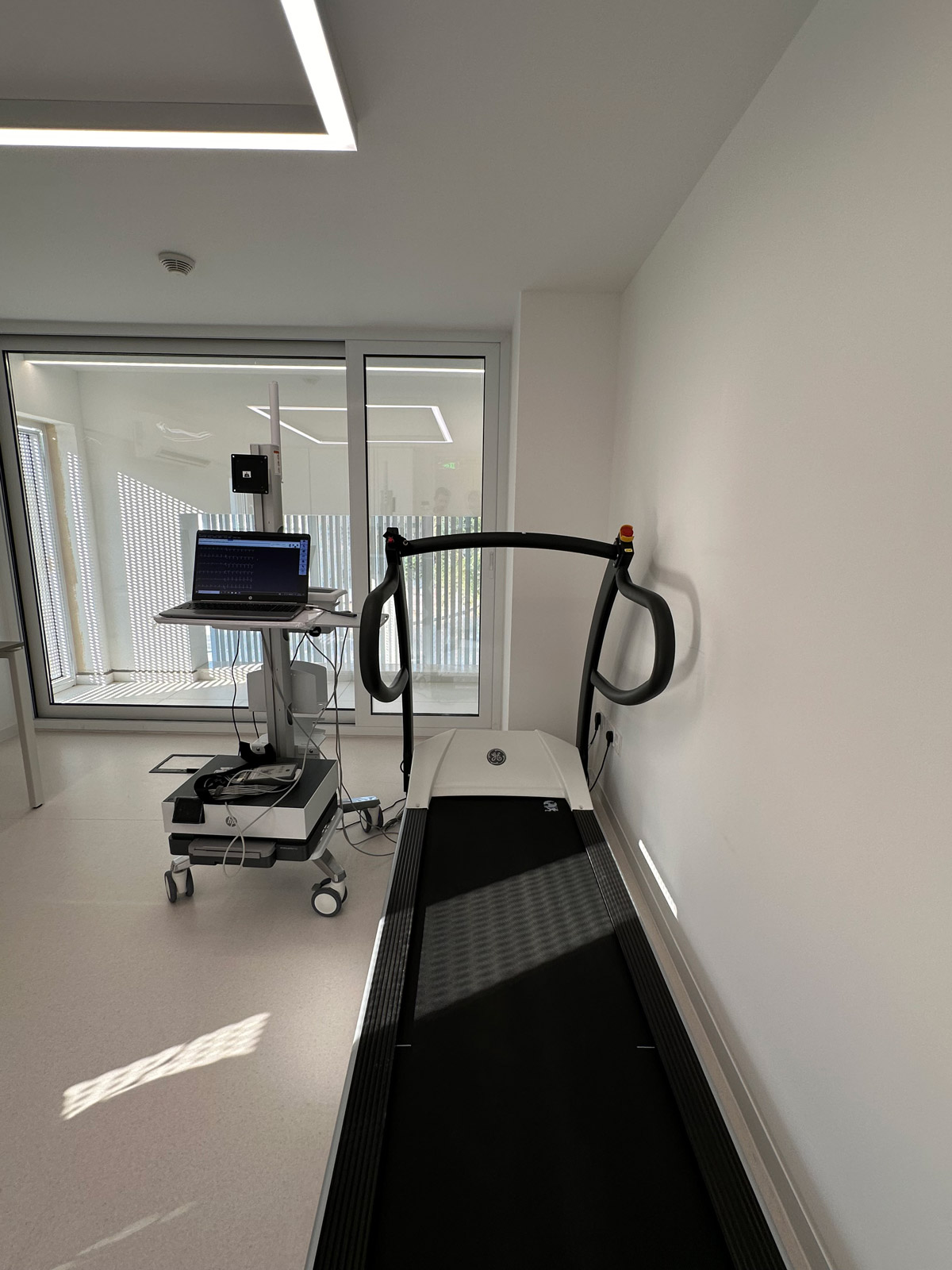
An exercise stress test is a test where the patient exercises on a treadmill whilst being under ECG monitoring and in the presence of a medical professional. The test is used to check how the heart responds to exercise and is often recommended in the presence of symptoms such as exertional chest pain or breathlessness on exercise.
During the test the doctor will gradually increase the level of difficulty and the objective is to get the heart rate up to a certain level which depends on the patient’s age. The patient will also be asked about symptoms throughout the test and the blood pressure will be recorded at regular intervals.
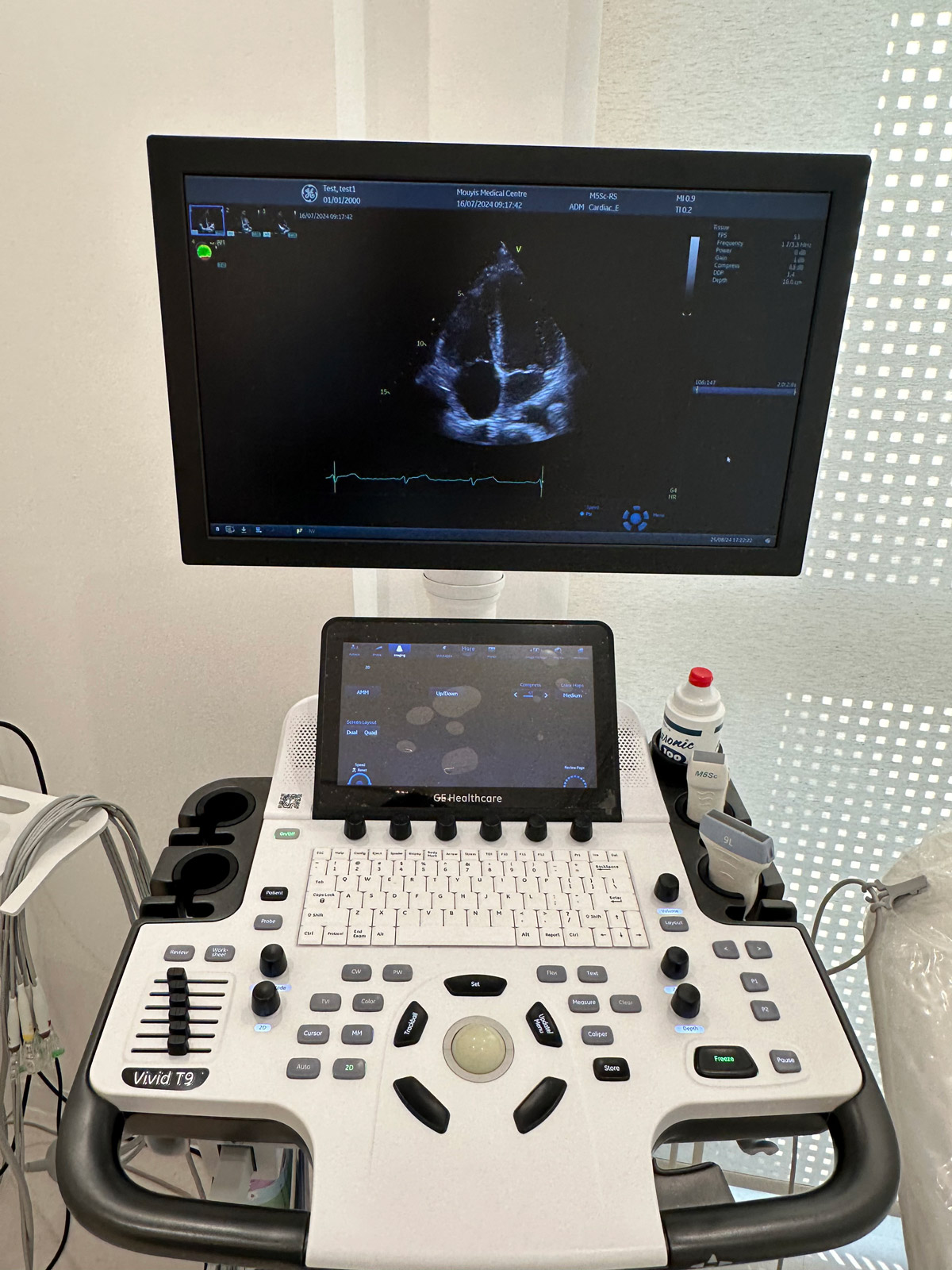
An echocardiogram is a specialized ultrasound test of the heart. It is one of the most important investigations in cardiology as it provides information on the structure and function of the heart as well as the flow of blood around the different chambers and through the heart valves. It usually takes anywhere from 15 to 30 minutes depending on how many measurements need to be taken.
To conduct an echocardiogram the patient needs to undress from the waist up to allow access to the chest wall. The echocardiogram is used to diagnose weakness of the heart muscle (heart failure), problems with heart valves and may need to be repeated as treatment for a condition is given.
Cardiac tests
Diagnosing for a Healthier Heart
We offer specialised non invasive cardiac investigations to help diagnose and treat a variety of cardiac conditions. All the tests are supervised by Dr Kyriacos Mouyis.
A Holter monitor is a small device that can record the heart rate and rhythm for a period from 24 hrs. up to 7 days. It is essentially a longer ECG that allows the doctor to make a diagnosis of heart rhythm problems where that is suspected.
The Holter monitor is attached with stickers onto 7 points on the body. It is important that the patient does not take a shower or a bath as this may cause the stickers to come off or the machine to malfunction.
Holter monitoring is often done for symptoms of palpitations or when the doctor suspects an arrhythmia may a be significant part of your disease process.
After fitting the monitor, you will need to return the next day to have it removed. Then the doctor needs to review and analyze the results before discussing them with you.
An exercise stress test is a test where the patient exercises on a treadmill whilst being under ECG monitoring and in the presence of a medical professional. The test is used to check how the heart responds to exercise and is often recommended in the presence of symptoms such as exertional chest pain or breathlessness on exercise.
During the test the doctor will gradually increase the level of difficulty and the objective is to get the heart rate up to a certain level which depends on the patient’s age. The patient will also be asked about symptoms throughout the test and the blood pressure will be recorded at regular intervals.
An echocardiogram is a specialized ultrasound test of the heart. It is one of the most important investigations in cardiology as it provides information on the structure and function of the heart as well as the flow of blood around the different chambers and through the heart valves. It usually takes anywhere from 15 to 30 minutes depending on how many measurements need to be taken.
To conduct an echocardiogram the patient needs to undress from the waist up to allow access to the chest wall. The echocardiogram is used to diagnose weakness of the heart muscle (heart failure), problems with heart valves and may need to be repeated as treatment for a condition is given.
Cardiac procedures
Your Heart, Our Expertise
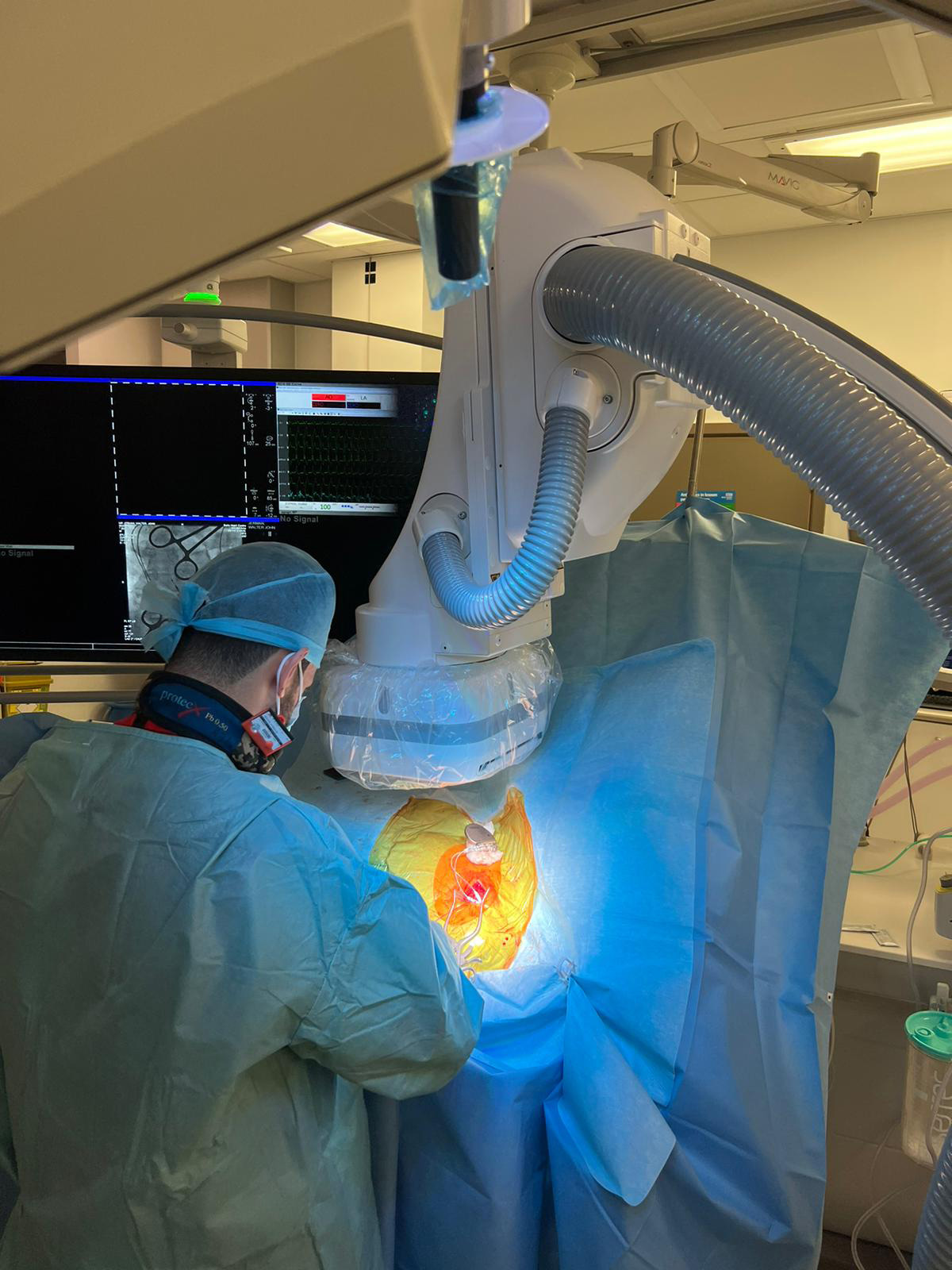
Dr Kyriacos Mouyis specializes in cardiac device procedures and followup. These procedures are offered to patients who would benefit after appropriate investigations.
A pacemaker is a small electronic device that is implanted in the upper chest and allows the treatment of slow heart rate (bradycardia) due to disease in the specialized conduction system of the heart. It comprises of a box (generator) that sits below the clavicle that is connected to 1,2 or 3 wires (depending on the clinical situation) that lead into the heart via the blood vessels. The wires can sense the electrical activity within the heart and initiate beating of the heart when necessary.
Pacemakers are inserted during a 1-1.5hr procedure under sedation and local anaesthesia inside a cardiac theatre called a catheterization laboratory.
The pacemaker generator battery lasts usually 8-10yrs and needs to be replaced after that time during a repeat procedure that usually lasts around 30 minutes.
Implantable Cardioverted Defibrillator is a specialized device that is implanted in patient at high risk of sudden cardiac death. Similar to a pacemaker it consists of a pulse generator and wires that lead into the heart (1, 2 or 3 wires depending on the clinical context) and it can sense life threatening heart rhythms and treat them using:
Pacing at a heart rate faster than the arrhythmia
Small electrical shock (cardioversion)
Larger electrical shock (defibrillation)
ICDs are implanted in the catheterization laboratory most commonly under sedation and local anaesthetic. It can take between 1hour to3 hours to complete the procedure depending on the exact type of device.
The ICD battery generally lasts from 8-10 years and needs to be replaced after that time. The repeat procedure generally takes 30-45minutes.
Following implantation cardiac devices need to be monitored by a specialist in clinic. A small electronic tool is placed over the site of the device and allows for communication between the device and a programming computer.
The parameters and settings of the device can then be checked and adjusted accordingly. The battery life of the device can also be checked to ensure it is replaced in due course. The frequency of the checks depends on the exact clinical context of the patient. Checks usually need to be conducted twice in the early period after device implantation and then at least every 6 months routinely.